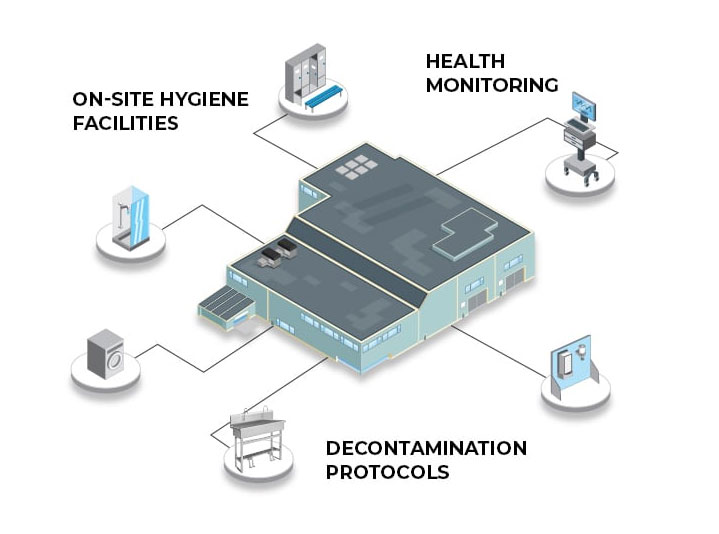
Employee and environmental safety is foundational to the North American lead battery industry. BCI members are committed to protecting workers, communities, and the environment through responsible practices that support a safe, reliable, and sustainable battery supply chain.
Employee Safety
Lead battery manufacturers and recyclers strive to exceed OSHA standards and are continually advancing to protect employees, the community...