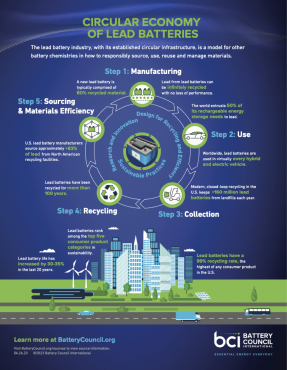
The lead battery industry’s established circular infrastructure has become a model for other battery chemistries – and industries – in how to responsibly source, use, reuse and manage materials.
Lead Battery | Sustainable
Today’s innovative lead batteries are key to a cleaner, greener future. They’re also the most environmentally sustainable battery...