
Today’s innovative lead batteries are key to a cleaner, greener future. They’re also the most environmentally sustainable battery technology and a stellar example of a circular economy model.

Today’s innovative lead batteries are key to a cleaner, greener future. They’re also the most environmentally sustainable battery technology and a stellar example of a circular economy model.
The lead battery industry is fostering global sustainability by evolving to meet the world’s growing energy demands.
In transportation, lead batteries reduce greenhouse gas emissions in vehicles with start-stop engines and help cut fuel consumption in those vehicles by up to 10%. In the renewable energy sector, lead batteries store wind and solar power, to ensure a steady supply of electricity, regardless of nature’s fluctuations.
Lead battery life has increased by 50% in the last 20 years. Collaborative research by Argonne National Laboratory and Missouri University of Science and Technology will further improve battery performance for green applications.
An established recycling infrastructure gives lead batteries a nearly 100% recycling rate. This steady supply of recycled lead battery components means a typical new lead battery is comprised of 80% recycled material.
Furthermore, the lead from these batteries can be infinitely recycled with no loss of performance. That greatly reduces the use of virgin materials, a key goal of the circular economy model.
In 2020, the U. S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) noted that the recycling rate of lead batteries exceeded that of other more well-known recycled products such as aluminum cans (50.4%), tires (40%), glass containers (31.3%), PET bottles (29.1%) and more. This high recycling rate contributes to the fact that on average, a new lead battery is comprised of 80% recycled material.
Lead batteries, with their 99% recycling rate, are infinitely recyclable, especially when compared to the fewer than 15% recycling rate of lithium-ion batteries. The lead battery industry’s commitment to efficient recycling methods ensures that lead batteries are an essential part of an energy storage mix to achieve a cleaner, greener future.


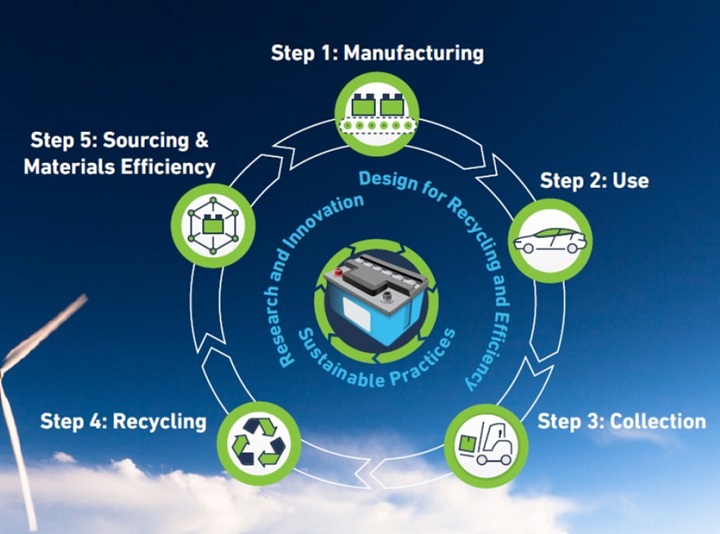
The state-of-the-art closed-loop process for recycling lead batteries that ensures lead batteries’ high rate of recycling has been recognized by the World Economic Forum and MIT’s Center for Transportation and Logistics as the world’s most successful example of a circular economy.
During the recycling process, the battery is broken down into its primary components: lead, plastic and acid, which are separated for reuse. The lead from spent batteries is melted, refined and poured into molds to create ingots (lead bricks) used to build new batteries. The plastic cover and case of a spent lead battery are crushed, cleaned, melted and formed into pellets to make new battery covers and cases. Spent acid is either recycled and reused in batteries, neutralized into water or converted into sodium sulfate, an odorless powder used in laundry detergents, textiles and glass.
After the recycling process is complete, materials are ready for reuse. On average, a new lead battery is comprised of 80% recycled material and the lead from these batteries can be infinitely recycled with no loss of performance. That, coupled with a recycling rate of nearly 100%, greatly reduces the use of virgin materials. This is a key goal of the circular economy, which reduces energy and greenhouse gas emissions.
A steady supply of recycled lead battery components allows lead battery manufacturers to use safe, sustainable practices to make new batteries. A nation-wide infrastructure, high recycling awareness and the economic value inherent in lead battery components ensures consumers and industries return spent lead batteries to the collection system which in turn supplies manufacturers with a reliable stream of materials for reuse.
Sustaining long-term success in our industry requires more than innovation. It requires strong financial stewardship, a values-driven culture, and a commitment to delivering for our customers and communities.