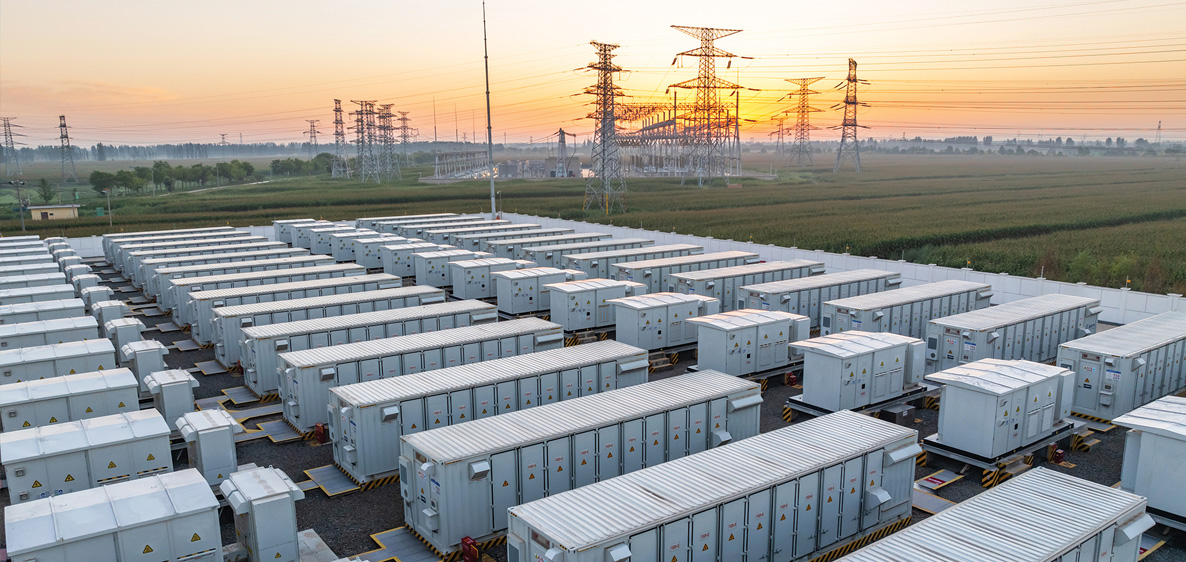
Stationary energy storage is critical to supporting a strong energy future – delivering the reliability, resilience, and sustainability our nation depends on. To meet diverse applications and growing demand, a variety of battery chemistries – including lead, flow, lithium, sodium, and zinc – is essential to support the evolving energy landscape.
Utility-grade Energy Storage
Utility-grade energy storage systems play a critical role in enhancing the reliability, efficiency, and sustainability of energy grids. By...